In today’s rapidly evolving artificial intelligence landscape, the protection of sensitive information and accuracy of AI responses have become paramount concerns. Extended Context Processing (XCP) represents a significant advancement in addressing these challenges by providing a comprehensive framework for context management in AI applications.
What is Extended Context Processing?
Extended Context Processing is an advanced system for managing context in AI applications that enhances privacy protection, information security, and precision in understanding content sent to language models. This sophisticated approach ensures that AI systems can maintain the delicate balance between utility and privacy, delivering accurate responses while safeguarding sensitive information.
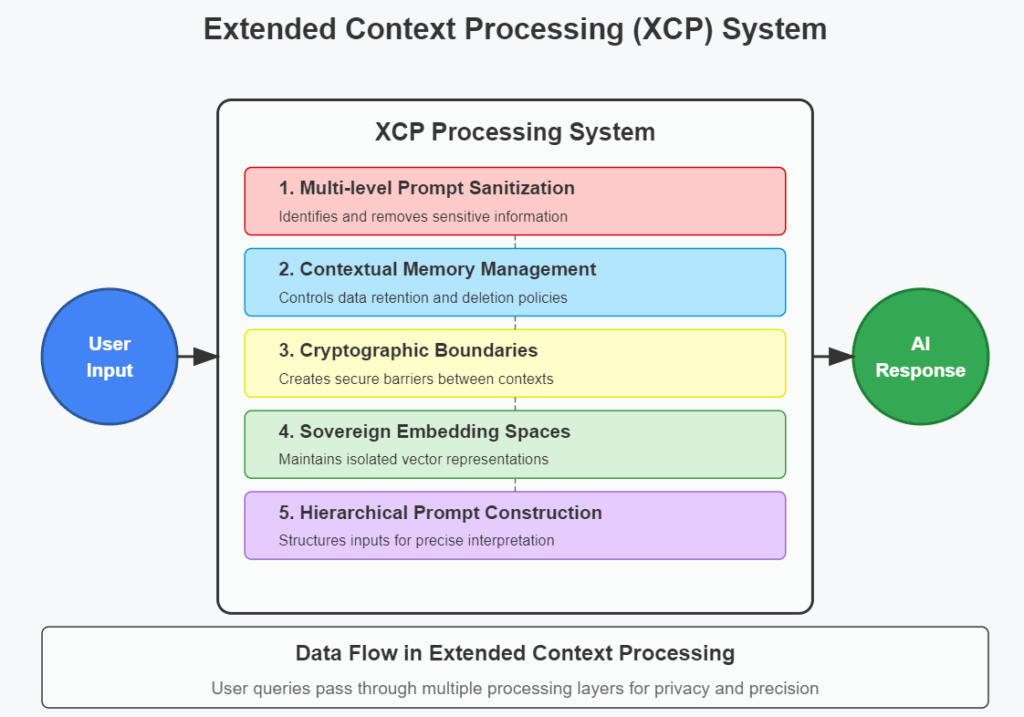
Key Components of XCP
1. Multi-level Prompt Sanitization
At the foundation of XCP lies a sophisticated filtering system that methodically processes user queries before they reach the language model. This multi-layered protection works as follows:
- The first layer identifies potentially sensitive information such as personal identification numbers, credit card details, addresses, and medical data
- Depending on sensitivity level, this information can be completely removed, masked (e.g., replaced with asterisks), or substituted with representative tokens that preserve context without revealing specifics
For example, the sentence “My ID number is 83052314796 and I live at 15 Flower Street, Apt. 4” might be transformed to “My ID number is [PERSONAL_DATA] and I live at [ADDRESS].” The model still understands the reference to personal data and an address without accessing the specific values.
2. Contextual Memory Management
XCP’s contextual memory management functions similarly to cache management in computer systems but with additional layers of intelligence and privacy rules. This system determines:
- Which information is relevant to current and potentially future conversations
- How long specific information should be stored in the model’s memory
- When and under what circumstances information should be deleted
Rules can be defined both globally (e.g., sensitive data is always removed after the session ends) and contextually (e.g., information about a user’s music preferences may be stored longer if the user frequently asks for music recommendations).
XCP can employ advanced algorithms to automatically classify information according to its sensitivity and significance, then apply appropriate storage and deletion protocols.
3. Cryptographic Verification of Information Boundaries
This layer of XCP utilizes cryptographic techniques to create impermeable barriers between different information contexts. It functions similarly to containerization in IT systems but at the level of language processing.
Each conversation context or document can be assigned a cryptographic signature (hash), enabling the system to quickly detect whether information comes from an authorized context. If the model attempts to reference information from another, unrelated context, the XCP system can block such action.
Technically, this can be implemented by creating cryptographically secured access tokens for specific blocks of contextual memory, where each reference to information requires verification of permissions.
4. Sovereign Embedding Spaces
Standard AI models often use a shared vector space to represent all data, which can lead to unintentional mixing of contexts (context collapse). Sovereign embedding spaces in XCP create separate, isolated vector representations for different categories of information or different clients/users.
Imagine that a traditional vector space is like a vast library where all books are on common shelves. Sovereign embedding spaces are like separate, closed rooms in this library, where each room contains only books belonging to a specific category or owner.
This isolation ensures that vector representations of one user’s data cannot “leak” into another user’s space, significantly increasing privacy and information security.
5. Hierarchical Prompt Construction
Hierarchical prompt construction is a methodical approach to formulating queries that improves precision in conveying intentions from humans to AI models. It’s like creating a multi-level instruction, where each level adds context and specificity.
At the highest level of the hierarchy are general guidelines regarding the purpose and context of the conversation. More detailed instructions, examples, and parameters appear at lower levels. This structure allows the model to better understand complex intentions and reduce the risk of misinterpretation.
For example, instead of a simple prompt like “Write an article about climate change,” a hierarchical construction might look like this:
- Level 1 (general purpose): Preparing an educational article about climate change
- Level 2 (context): Article intended for high school students with basic scientific knowledge
- Level 3 (detailed guidelines): Focus on anthropogenic causes, current effects, and possible solutions
- Level 4 (style parameters): Accessible language, objective tone, length 1000-1500 words
This structure minimizes the risk of the model going in an unexpected direction or misinterpreting user intentions.
Practical Applications of XCP
Extended Context Processing finds applications in particularly sensitive areas, such as:
- AI systems used in healthcare, where patient data confidentiality is crucial
- Legal and financial applications operating on sensitive personal and business data
- Corporate AI systems processing documents containing proprietary information
- Educational platforms where maintaining student data privacy is important
The Future of Context Processing in AI
As AI systems become more integrated into sensitive areas of our lives and businesses, technologies like XCP will play an increasingly vital role in ensuring these systems remain trustworthy and secure. By addressing the dual challenges of privacy protection and contextual accuracy, XCP represents a significant step toward creating AI systems that are not only intelligent but also responsible and trustworthy in terms of privacy protection and information security.
While specific implementations of XCP may vary across organizations, the underlying principles represent the direction in which responsible AI development is heading. As regulatory frameworks around AI continue to evolve, frameworks like XCP will likely become standard practice in the industry, helping to build user trust and ensure compliance with increasingly stringent privacy regulations.
This article provides an overview of the Extended Context Processing framework for AI systems, highlighting its key components and applications in enhancing privacy and precision in artificial intelligence applications.




